SHARE THIS ARTICLE
What is DePIN – Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Network?
Our world relies on a complex network of infrastructure – from power grids and communication towers to data centers and transportation systems. These centralized models have served us well, but they also face inherent limitations.
Firstly, traditional infrastructure can be incredibly expensive to build and maintain. This results in limited access, particularly in remote or underserved areas. Additionally, centralized systems create single points of failure, making them vulnerable to outages and disruptions. For instance, the consequences of a power grid shutdown impacting an entire city or a critical data center experiencing a cyberattack can be widespread and costly.
However, a new approach is coming up on the horizon. Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks, or DePINs, utilize blockchain development services to revolutionize how we build and manage infrastructure. DePINs create open marketplaces where individuals and businesses can contribute their physical resources – like home solar panels or unused storage space – to a shared network.
This peer-to-peer approach holds immense potential. By allowing anyone to participate, DePINs have the power to democratize access to essential infrastructure and foster a more efficient and resilient ecosystem. Businesses can benefit from lower operational costs and a wider pool of resources, while individuals gain the opportunity to earn rewards for sharing their underutilized assets. As DePIN technology matures, we can expect to see a wave of innovation that reshapes the way we interact with the infrastructure that underpins our daily lives.
Understanding DePINs in Detail
DePins or Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks represent a revolutionary approach to building and managing physical infrastructure. Unlike traditional models controlled by centralized entities, DePINs utilize blockchain technology and decentralization principles to create open, collaborative networks.
 The Core Principles of DePins
The Core Principles of DePins
DePINs operate on a set of core principles that redefine how infrastructure is built and managed.
Decentralization and Community Governance
Unlike traditional, top-down models, DePINs harness blockchain technology to create decentralized networks. This means there's no single authority controlling the network. Instead, a community of participants governs the network through voting mechanisms on the blockchain. This leads to a more democratic and transparent decision-making process.
Crowdsourcing and Peer-to-Peer Infrastructure Models
DePINs function through crowdsourcing, where individuals and businesses contribute physical resources like Wi-Fi routers, storage space, or energy capacity to the network. These resources are then shared in a peer-to-peer (P2P) fashion, eliminating the need for centralized infrastructure providers.
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)
DLT, the core principle behind blockchain app development, empowers DePINs with unmatched security and transparency. All network transactions are replicated across a vast network of computers, making them virtually tamper-proof. This fosters trust and accountability among participants, eliminating the need for a central authority to monitor activity.
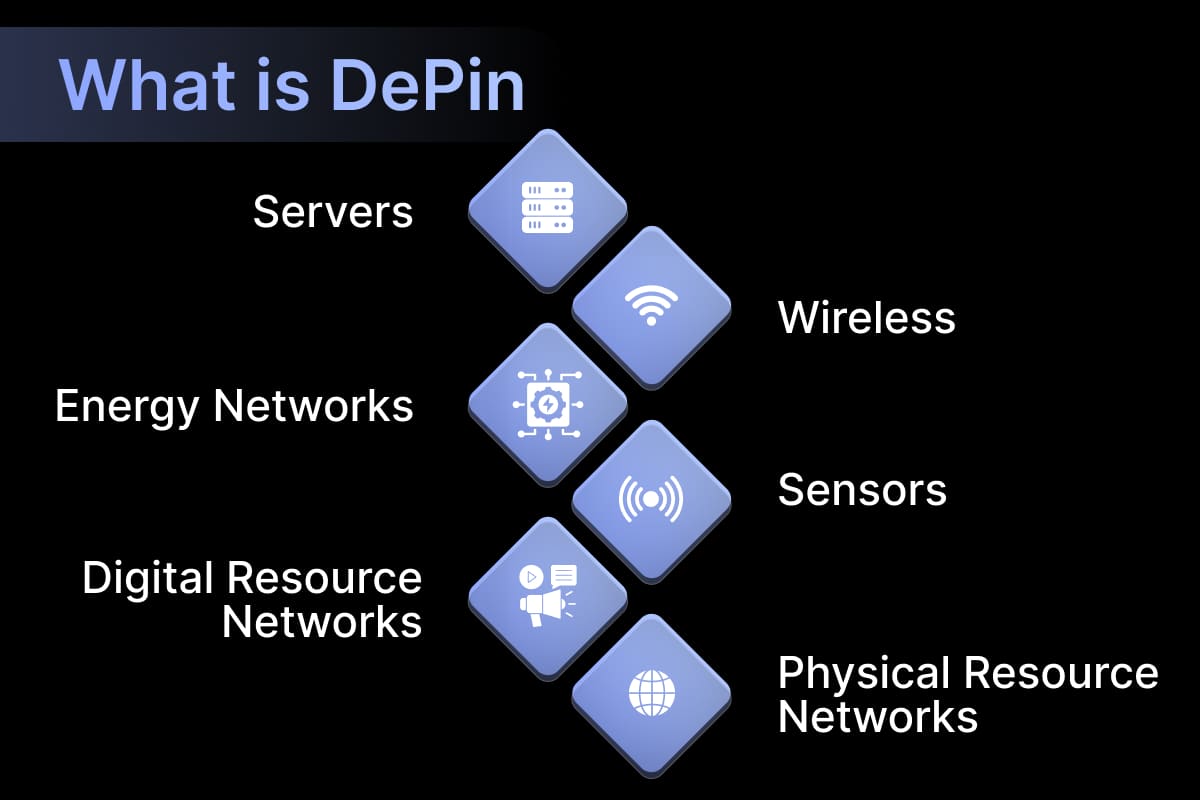
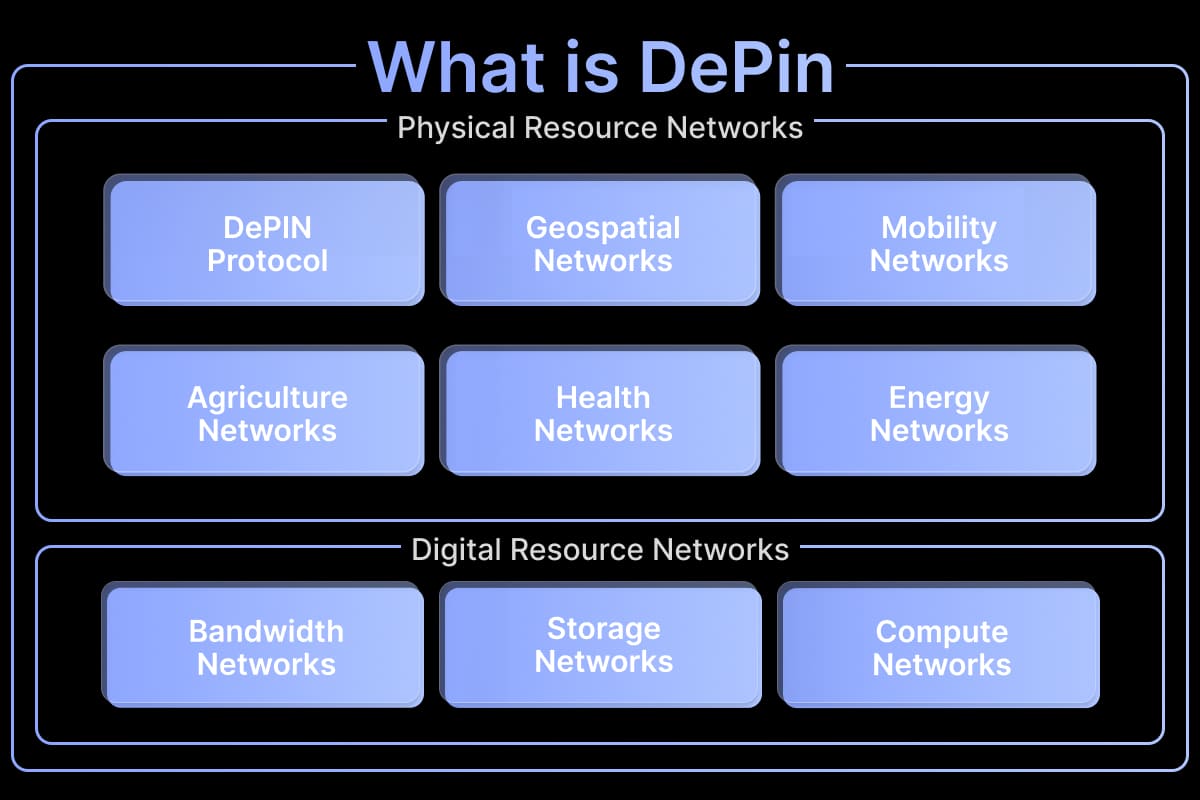
Categories of DePINs:
DePINs cater to a wide range of infrastructure needs, and understanding their categories helps us grasp their functionalities.
-
Physical Resource Networks (PRNs): These DePINs utilize physical resources tied to a specific location. For instance, consider a network of home Wi-Fi routers providing internet access, or unused storage space from individuals contributing to a decentralized cloud. Even electric vehicle charging stations built and managed through DePIN models fall under this category.
-
Digital Resource Networks (DRNs): DRNs deal with digital resources that are not tied to a specific location and can be accessed remotely. Think of unused computing power from personal computers being used for complex tasks, or geographically distributed data storage accessed through a DePIN network.
How DePINs Work
DePINs rely on several key technological components to function.
Blockchain as the Foundation
The core of any DePIN network is the underlying blockchain. This distributed ledger technology (DLT) ensures all transactions and network data are immutably recorded and readily accessible to all participants. This enhances trust and transparency within the DePIN ecosystem.
Smart Contracts
These self-executing agreements built on the blockchain, automate crucial network functions. These contracts define the terms for resource contribution, user access, and token rewards. For instance, a smart contract might automatically credit a user's account with tokens whenever their home Wi-Fi router provides internet access to others in the network.
Crypto Tokens
Crypto tokens serve as the fuel that drives DePIN networks. They incentivize users to contribute resources and participate in network activities. Users pay tokens to access services, while resource providers earn tokens as rewards. This token-based economy promotes a sustainable and self-governing network ecosystem.
Integration with the Internet of Things (IoT)
DePINs can integrate with the Internet of Things (IoT) to create a dynamic and responsive infrastructure network. IoT devices can collect real-time data on resource availability and usage, enabling the network to optimize resource allocation and service delivery. Specific protocols like LoRaWAN for low-power wide-area communication can be employed to facilitate secure and efficient data exchange between devices and the DePIN network.
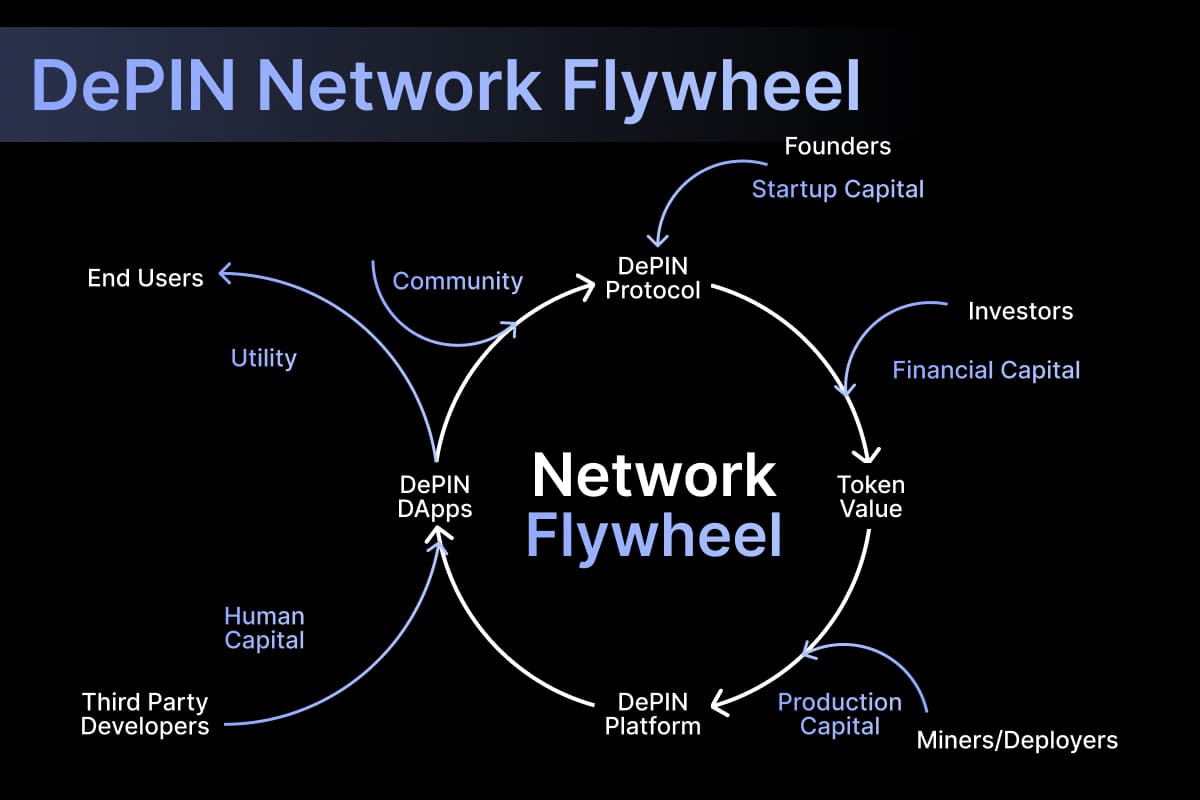
The Building Blocks of DePINs
DePINs function through a unique interplay of three core components: physical infrastructure, open marketplaces, and incentive mechanisms powered by crypto tokens.
Physical Infrastructure
DePINs can comprise a wide range of physical infrastructure types, essentially any resource that can be digitized and shared within a network. Here are some prominent examples.
-
Data Storage: DePINs can create decentralized cloud storage solutions. Individuals with unused storage space on their computers can contribute it to the network, offering a more affordable and geographically distributed alternative to traditional cloud providers.
-
Wireless Networks: DePINs facilitate a network of Wi-Fi hotspots powered by individuals sharing their home routers. These are secure connections and allow users to pay for access using crypto tokens.
-
Energy Grids: DePINs can pave the way for peer-to-peer energy trading. Individuals with solar panels or other renewable energy sources can sell excess energy back to the grid, while others can purchase clean energy at competitive rates.
-
Compute Power: DePINs can create decentralized compute networks. Individuals can contribute their unused processing power to tackle complex computational tasks, offering a more scalable and cost-effective alternative to traditional cloud computing resources.
-
LoRaWAN Networks: DePINs can facilitate the creation of low-power, wide-area networks for various applications. These networks, utilizing protocols like LoRaWAN, can be used for environmental monitoring, smart city infrastructure, and industrial automation purposes.
Open Marketplaces
DePINs operate as open marketplaces where individuals and businesses can contribute their physical resources and access services offered by the network. These marketplaces function with transparency and efficiency.
-
Resource Contribution: Users can easily register their physical resources on the DePIN network. The process is optimized and user-friendly, allowing for hassle-free integration of new resources.
-
Service Access: Users can discover and access services offered by the network in real-time. This could be anything from additional storage space to a nearby electric vehicle charging station.
-
Price Setting and Negotiation: Depending on the specific DePIN network, users and providers may have some flexibility in setting prices for resource contribution and service access.
Incentive Mechanisms
Crypto tokens play a crucial role in incentivizing user participation and driving network growth within DePINs. Here's how the incentive structure works.
-
Rewarding Infrastructure Providers: Users who contribute resources to the network are rewarded with crypto tokens. This could be based on the amount of storage space offered, bandwidth shared, or processing power contributed.
-
Token Utility: Earned tokens can be used within the DePIN network to pay for services like additional storage or faster internet access. They may also have value outside the network and be traded on cryptocurrency exchanges.
-
Token Economics: DePIN networks carefully design token economics to ensure long-term sustainability. This involves factors like token supply, distribution mechanisms, and potential token-burning strategies to control inflation.
Community Governance
DePINs operate on the principle of decentralization, extending beyond just resource allocation and service access. Community governance allows DePIN participants to collectively make decisions about the network's future direction. This promotes a sense of ownership and ensures that the network evolves to meet the needs of its users.
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) offer a promising framework for DePIN governance. DAOs are internet-native communities with transparent rules encoded on the blockchain. DAO participants, typically identified by their ownership of the DePIN's crypto token, can vote on proposals that affect the network, such as:
-
Upgrades to the DePIN protocol
-
Integration of new infrastructure types
-
Allocation of network resources
-
Adjustments to Token Economics
By utilizing DAOs, DePINs can ensure fair and transparent decision-making, leading to a collaborative environment where all participants have a voice in shaping the network's future.
Advantages and Challenges of DePINs
DePINs offer a glimpse into a future where infrastructure is built and managed in a more efficient, transparent, and democratic way. However, like any emerging technology, DePINs face their own set of challenges that need to be addressed. Let's explore both the advantages and hurdles associated with DePINs in more detail.
Advantages of DePINs
- Increased Efficiency and Scalability
DePINs tap into the vast, underutilized resources of individuals and businesses. Instead of relying on centralized entities to build massive data centers or lay miles of fiber optic cable, DePINs can leverage a distributed network of spare storage space, home Wi-Fi routers, or even idle processing power from personal computers. This distributed approach has the potential to optimize infrastructure development, making it more efficient and adaptable to meet growing demands. - Enhanced Transparency and Trust
Blockchain technology forms the backbone of DePINs, ensuring all transactions are secure and verifiable on a shared ledger. Every interaction, from resource contribution to service usage, is permanently recorded and accessible to all participants. This leads to a high degree of trust and accountability within the network. Unlike traditional models where users rely on a central authority to manage resources, DePINs eliminate the need for intermediaries, allowing users to have greater control and transparency over their data and interactions. - Democratization of Infrastructure
DePINs help individuals to become active participants in the infrastructure they rely on every day. By contributing their underutilized resources to the network, individuals can earn crypto tokens as rewards. These tokens can be used to pay for services within the DePIN network or even traded on cryptocurrency exchanges. This not only creates new income opportunities for individuals but also allows them to have a stake in the infrastructure they use, promoting a sense of ownership and community. - Potential for Cost Reduction
Decentralized models have the potential to optimize operational processes and reduce overhead costs associated with traditional infrastructure management. By eliminating the need for intermediaries and central authorities, DePINs can potentially offer more affordable infrastructure services for users. Additionally, by utilizing a distributed network of resources, DePINs can optimize resource allocation and utilization, further contributing to cost reductions.
Challenges of DePINs
- Technical Complexity
Building and maintaining secure and scalable DePIN networks requires advanced technical expertise. Integrating physical infrastructure with blockchain technology is a complex task that necessitates specialized knowledge in areas like cryptography, distributed systems, and network security. As a result, it’s advisable to collaborate with a reputed blockchain consulting company for your DePIN project. Additionally, designing robust incentive structures that motivate user participation and ensure the long-term sustainability of the DePIN network requires careful economic modeling and ongoing adjustments. - Regulatory Uncertainty
The legal frameworks surrounding DePINs and cryptocurrencies are still evolving. Many regulatory bodies are still grappling with how to classify and regulate these emerging technologies. This uncertainty can deter potential participants, such as businesses and investors, from entering the DePIN space. As regulatory frameworks become clearer, DePINs will likely see wider adoption and mainstream acceptance. - Network Effects
DePINs, like many network-based technologies, face the challenge of attracting a critical mass of users to establish strong network effects. The initial stages of DePIN development might be hindered by a limited user base. Without a large pool of resource providers and service users, the value proposition of DePINs might be limited. Overcoming this challenge requires effective user acquisition strategies and building a strong ecosystem that incentivizes early adopters and promotes network growth. - Security Concerns
Decentralized systems can be vulnerable to cyberattacks. While blockchain technology offers inherent security benefits through its distributed ledger architecture, DePINs still need to prioritize robust security measures to protect user data and network integrity. This includes implementing secure communication protocols, employing strong encryption techniques, and conducting regular security audits to identify and address potential vulnerabilities.
Real-World Applications of DePINs
DePINs are not just theoretical concepts; they are actively being implemented across various industries, demonstrating their real-world potential.
Telecom
DePINs are enabling the creation of decentralized WiFi networks. Individuals can share their unused Wi-Fi bandwidth with the network, expanding internet access in underserved areas or offering alternative connectivity options in densely populated locations. Users can discover and connect to these shared hotspots through DePIN mobile applications, often paying for access with crypto tokens earned through the network. Projects like Helium and Nodle are actively building these decentralized wireless networks.
Energy
DePINs are transforming the energy sector by facilitating peer-to-peer energy trading. Imagine a network where individuals with solar panels or other renewable energy sources can sell excess electricity back to the grid. DePINs create a secure and transparent platform for these transactions, leveraging smart contracts to automate energy exchange and ensure fair compensation for providers. This helps individuals become active participants in the energy market and promotes a more sustainable and distributed energy ecosystem. Projects like PowerLedger and SunCoin are pioneering this approach to energy management.
Mobility
DePINs are facilitating a more accessible and user-friendly electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure. DePIN networks can connect individuals with spare charging capacity (e.g., home garages with unused outlets) to EV owners. Users can locate and pay for charging services through the DePIN platform, using crypto tokens earned by contributing to the network. This collaborative approach can significantly expand the availability of EV charging stations, accelerating the transition towards a more sustainable transportation future. Projects like PlugShare and WePower are building DePIN-based EV charging solutions.
Beyond these examples, the potential applications of DePINs extend even further:
-
Logistics: DePINs can create decentralized storage networks for logistics companies, allowing them to utilize unused storage space from individuals or businesses.
-
Healthcare: DePINs can facilitate secure and transparent data sharing between patients and healthcare providers, potentially improving healthcare delivery and research efforts.
-
Environmental Monitoring: DePINs can integrate with sensor networks to collect real-time environmental data on air quality, weather patterns, or noise pollution, aiding communities in monitoring their environment and taking collective action.
Live DePIN Projects in the Market
Several DePIN projects are already making waves in the industry.
Filecoin
Filecoin utilizes a global network of user-powered storage to create a decentralized alternative to traditional cloud storage providers. Users can contribute unused storage space on their computers or hard drives and earn FIL tokens in return. Filecoin offers several advantages over traditional cloud storage.
-
Data is stored across a distributed network, eliminating the risk of a single point of failure.
-
By leveraging unused storage from individuals, Filecoin can offer more affordable storage solutions compared to centralized providers.
-
Users have more control over their data, as they choose who can access it and set the storage price.
Render
Render allows users to contribute their unused computing power for complex tasks like video rendering or 3D animation. Users can share their graphics processing units (GPUs) through the Render Network and earn RNDR tokens in return. Content creators can then access this distributed rendering power to process their projects at a fraction of the cost of traditional cloud rendering services. This benefits both content creators who can produce high-quality videos and animations more affordably, and everyday users who can earn passive income by contributing their unused computing resources.
Theta Network
Theta Network focuses on video streaming, creating a decentralized network where users can contribute bandwidth to improve content delivery and earn THETA tokens. Viewers can also benefit from a smoother streaming experience with reduced buffering and potentially lower costs. Theta Network utilizes a novel token economics model that incentivizes users to share their bandwidth and resources to improve the overall network performance. Content creators and distributors can harness Theta Network to deliver high-quality video content to a global audience, while viewers can enjoy a more reliable and efficient streaming experience.
Final Takeaways
DePINs hold immense promise for reshaping how we build and manage infrastructure. By harnessing blockchain technology and decentralization principles DePINs have the potential to revolutionize various sectors, from telecommunication and energy to transportation and environmental monitoring. These decentralized networks can offer greater efficiency, transparency, and accessibility in infrastructure development, helping individuals become active participants in shaping the infrastructure of tomorrow.
At Codezeros, we are a leading blockchain development company committed to playing a pivotal role in the DePIN revolution. We are actively developing innovative solutions that leverage DePIN technology to create a more sustainable, collaborative, and user-centric infrastructure ecosystem. We possess the required expertise in developing DePIN solutions for a specific industry and building core DePIN technologies, along with actively participating in DePIN communities. Feel free to reach out to learn more about DePIN and other blockchain solutions.
Post Author

Explore Deep's insightful blog posts that help businesses stay ahead of the curve, explore new possibilities, and unlock the full potential of blockchain technology
Gain expert insights into your decentralized network project with Codezeros.
Decentralized networks are the future and blockchain technology lies at its core. Connect with us at Codezeros to leverage the expertise of our dedicated Blockchain developers and consultants for optimal project execution.



