SHARE THIS ARTICLE
What Is the Ethereum Cancun- Deneb Upgrade?

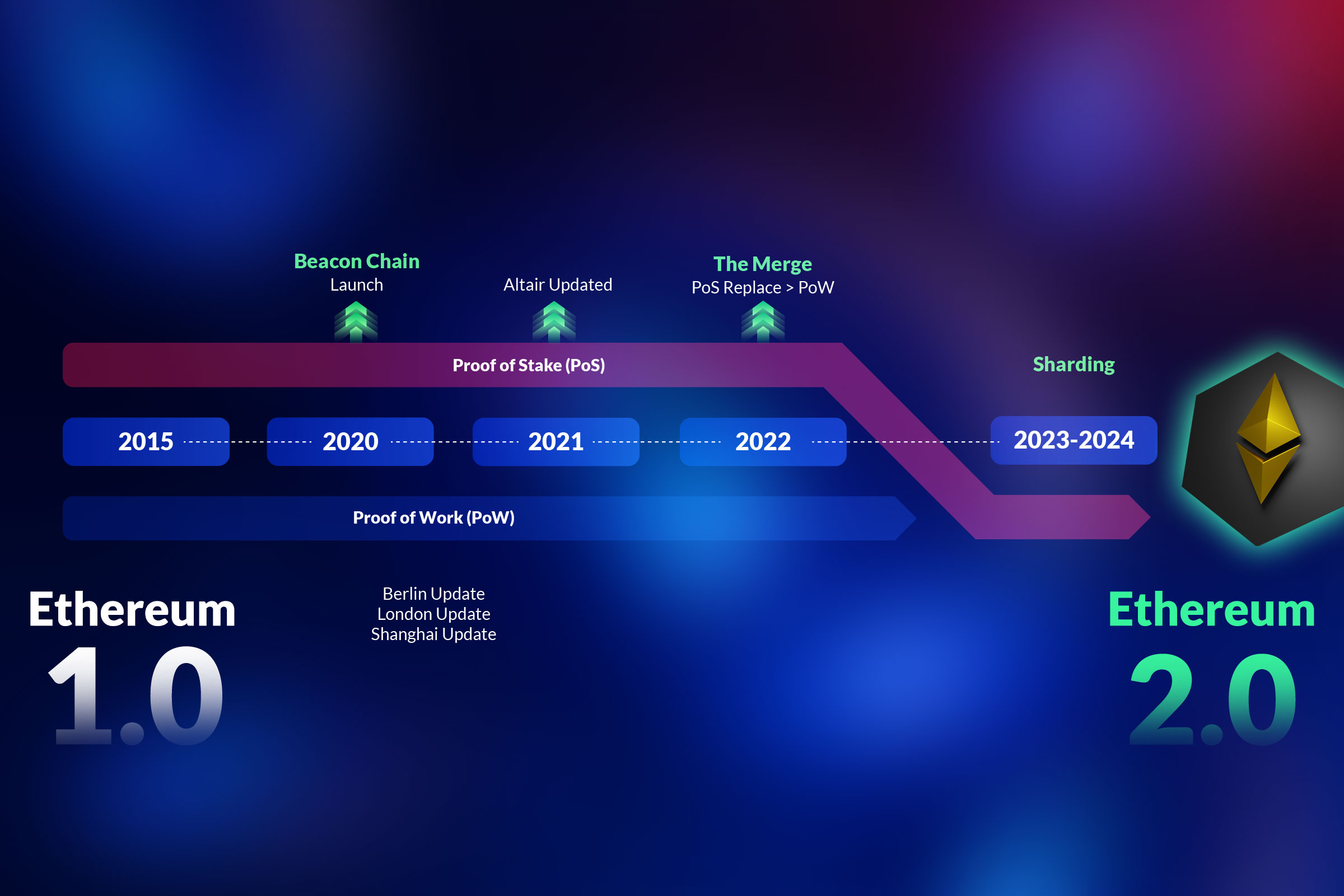
Ethereum, the world’s leading smart contract platform, is undergoing a major transformation to enhance its performance, security, and usability. The Ethereum Cancun-Deneb upgrade, also known as Dencun, is the latest milestone in this journey, introducing a new concept called proto-danksharding that aims to boost scalability, reduce gas fees, and support Layer 2 solutions.
A Brief Overview of the Canun-Deneb Upgrade
The Cancun-Deneb upgrade is the culmination of a series of previous upgrades that have improved various aspects of the Ethereum application development. These include the Shanghai upgrade, which introduced the Beacon Chain and the transition to Proof of Stake; the Berlin upgrade, which implemented four Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs) to optimize gas usage and prevent denial-of-service attacks; and the London upgrade, which introduced the EIP-1559, a mechanism to make gas fees more predictable and burn a portion of the transaction fees.
The Cancun Upgrade for Enhancing Scalability
The Cancun upgrade improves the execution layer of Ethereum, which processes transactions and smart contracts. It introduces EIP-1234, which reduces the block reward from 3 ETH to 2 ETH, slowing down Ethereum’s inflation rate and aligning it with Bitcoin’s. EIP-1234 also delays “the difficulty bomb” for approximately 12 months, ensuring a smooth transition to Ethereum 2.0. This way, the Cancun upgrade balances the interests of the miners, the users, and the developers.
The Deneb Upgrade for Improving Consensus and Security
The Deneb upgrade targets the consensus layer of Ethereum, which maintains the security and integrity of the network. It introduces EIP-2322, which upgrades the PoS consensus algorithm, making it more robust, efficient, and attractive for validators.
Core EIPs
The Cancun-Deneb upgrade is based on the following core EIPs:
-
EIP-4844
-
EIP-1153
-
EIP-4788
-
EIP-6780
These EIPs focus on enhancing the execution layer of the Ethereum network, which is responsible for processing transactions and smart contracts. The most notable feature of the Cancun-Deneb upgrade is proto-danksharding, which is a precursor to full data sharding. Proto-danksharding allows the network to store large data packets or “blobs” that can be used by Layer 2 solutions to increase throughput and lower costs.
EIP-4844: Shard Blob Transactions
EIP-4844 proposes a new transaction type that carries a large amount of data, called a blob, which is not processed by the EVM but can be verified by a cryptographic commitment. This transaction format is compatible with the future sharding system, where each shard will have its own blobs and transactions.
The goal of this EIP is to increase the data availability of Ethereum in a simple and future-proof way. Data availability is crucial for scaling solutions that rely on the security and decentralization of the base layer, such as rollups, channels, and sidechains. However, the current data capacity and throughput of Ethereum are constrained by the block size and gas limit.
To overcome this limitation, EIP-4844 introduces the concept of danksharding and proto-danksharding, which are two ways to enhance scalability, lower gas fees, and support Layer 2 solutions by using data blobs and blob-carrying transactions.
Danksharding:
Partitioning the Blockchain Danksharding is a term that describes the concept of dividing the Ethereum blockchain into smaller parts called “blobs.” A blob is a large chunk of data (~125 kB) that is cheaper than the current calldata, which is the memory used to store transaction data. Blob-carrying transactions are similar to regular Ethereum transactions but with an additional blob of data attached.
By implementing danksharding, the upgrade aims to increase the capacity of the Ethereum network and reduce transaction fees. This partitioning technique allows for parallel processing of transactions and smart contracts, resulting in improved scalability and throughput.
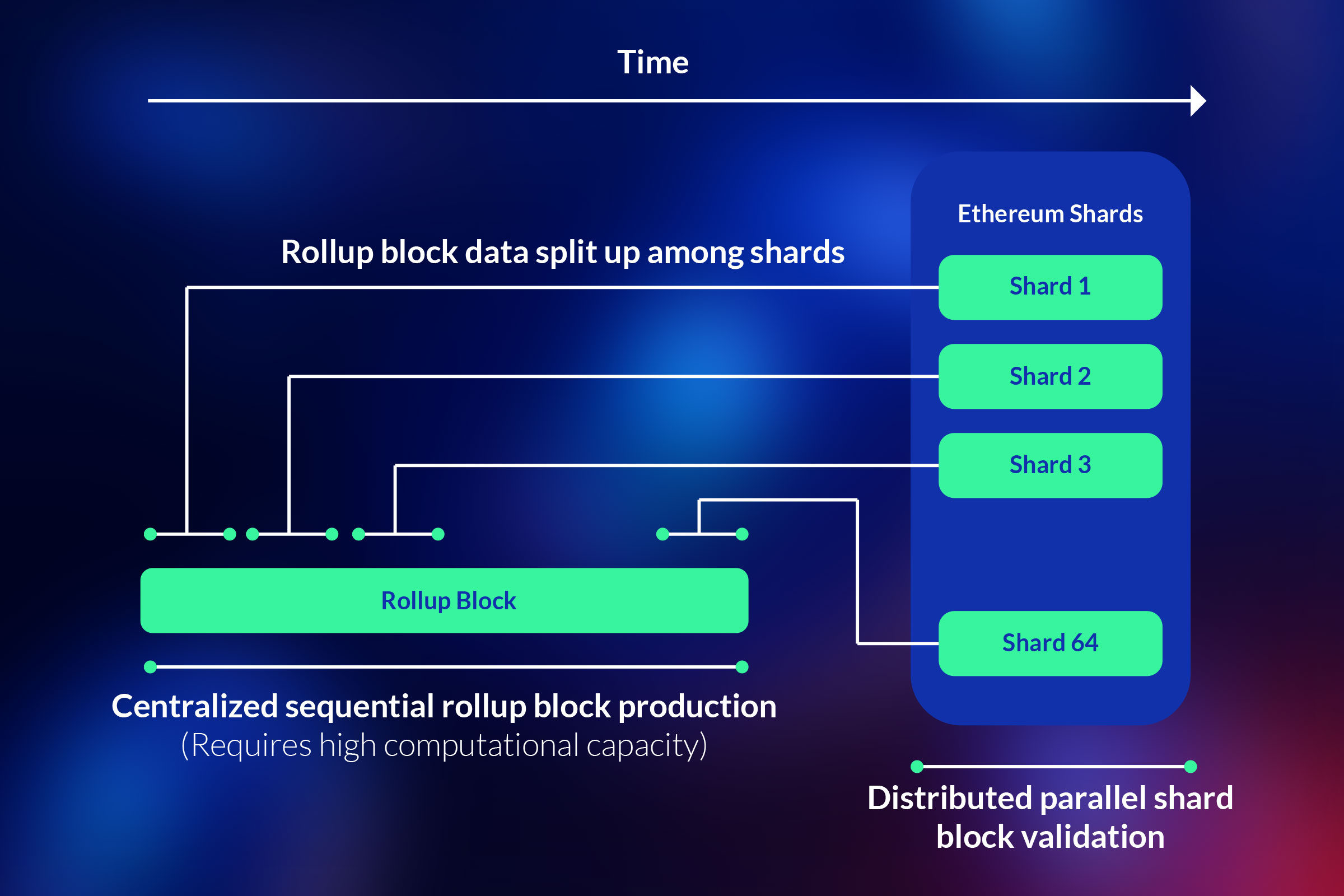
Proto-Danksharding:
Expanding Storage Capacity Proto-danksharding, also known as EIP-4844, is a feature in the Ethereum Cancun-Deneb Upgrade that builds upon the concept of danksharding. It expands the capability of danksharding by creating more space for storing data within the Ethereum network. This enables more efficient processing of large amounts of data and further enhances scalability.
Proto-danksharding has significant implications for layer-2 rollups, which are a type of Layer 2 solution that bundle many transactions together and submit them to the base layer as a single transaction. This reduces the load on the base layer and increases the throughput. However, rollups still need to store the data on the base layer for security and verifiability reasons. Making more space available for data blobs reduces gas fees associated with using rollups, leading to a better experience for Ethereum users.
Danksharding and proto-danksharding address one of the key challenges facing the Ethereum network: scalability. These innovations allow for the network to handle more transactions and smart contracts, facilitating the growth and adoption of decentralized applications (dApps) built on the Ethereum platform.
The use of blobs in danksharding and proto-danksharding has several benefits for the Ethereum network and its users:
-
Enhanced Scalability: Dividing the blockchain into smaller blobs allows for parallel processing, enabling the Ethereum network to handle more transactions and smart contracts. This improves scalability, reduces congestion, and lowers fees.
-
Efficient Resource Utilization: Segregating the blockchain into independent blobs optimizes resource allocation within the network. Each blob can focus on processing specific types of transactions or executing specific smart contracts, saving processing power and storage.
-
Flexibility and Modularity: The use of blobs provides a modular structure to the Ethereum network. It allows for adding or removing blobs as per the needs of the network, enabling future scalability upgrades to be implemented more easily.
The concept of blobs in danksharding and proto-danksharding introduces a more efficient and scalable framework for the Ethereum blockchain. By partitioning the network and expanding storage capacity within each blob, danksharding enhances transaction processing speed, reduces fees, and supports the growth of decentralized applications on the Ethereum platform.
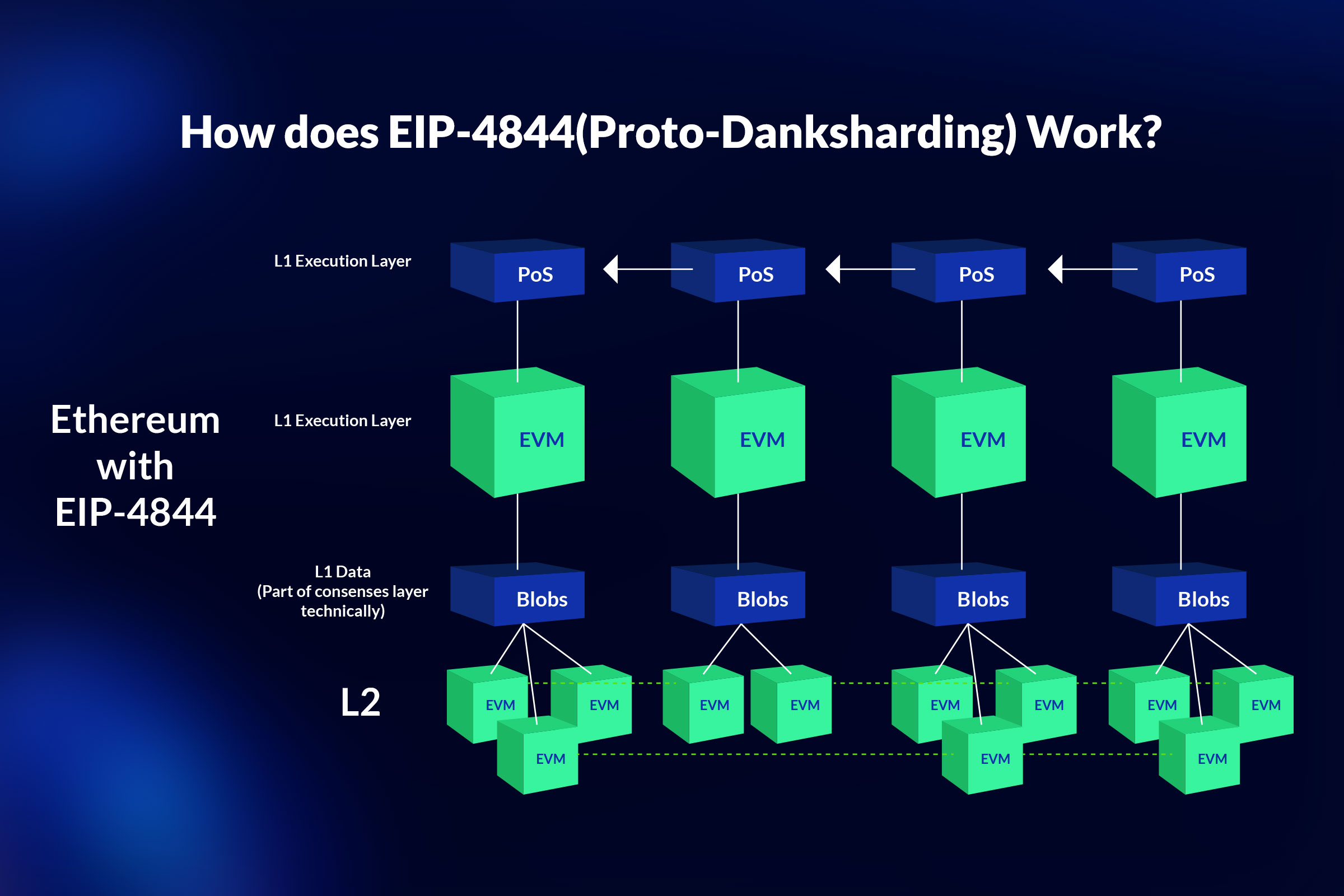
Proto-danksharding differs from full danksharding in several ways:
-
Proto-danksharding does not require any changes to the network topology or the consensus protocol, whereas full danksharding will introduce new types of nodes, such as shard validators and crosslink committees, and new types of messages, such as shard blocks and crosslinks.
-
Proto-danksharding does not increase the state size or the complexity of the execution layer, whereas full danksharding will require the execution layer to manage multiple shard states and coordinate cross-shard transactions.
-
Proto-danksharding does not provide any computation scalability or parallelism, whereas full danksharding will enable the network to process transactions and smart contracts on different shards simultaneously.
Proto-danksharding has several advantages over the current state of the network:
-
It increases the data capacity and throughput of the network by allowing more data to be stored in each block. This can improve the user experience and the performance of applications that require large amounts of data, such as decentralized exchanges, social media platforms, and gaming platforms.
-
It reduces the gas fees for data storage by introducing a cheaper alternative to calldata. This can lower the barriers to entry and the operational costs for users and developers who want to use the network for data-intensive applications.
-
It enables modular scalability for Layer 2 solutions, which can use the data blobs to perform computations off-chain and only submit proofs on-chain. This can increase the scalability and privacy of applications that use rollups, channels, or sidechains, as well as reduce the load and congestion on the main chain.
-
It enhances the security and decentralization of the network by preventing data withholding attacks and enabling fraud proofs. Data withholding attacks are a type of attack where a malicious actor hides or deletes some data that is needed to verify the validity of a transaction or a smart contract. Fraud proofs are a type of mechanism that allows anyone to challenge the validity of a transaction or a smart contract by providing evidence of fraud. Proto-danksharding ensures that all data blobs are available and accessible on the beacon chain, making data withholding attacks impossible and fraud proofs feasible.
Some examples and use cases of proto-danksharding are:
-
Optimistic rollups can use data blobs to store the state roots and transaction data of their off-chain execution environments, reducing the cost and latency of verifying and finalizing transactions.
-
ZK rollups can use data blobs to store the ZK-SNARK proofs and public inputs of their off-chain computations, increasing the scalability and privacy of their applications.
-
State channels can use data blobs to store the state updates and signatures of their off-chain interactions, improving the efficiency and reliability of their dispute-resolution mechanisms.
-
Sidechains can use data blobs to store the block headers and Merkle proofs of their off-chain consensus protocols, enhancing the interoperability and security of their bridges.
EIP-1153: Transient Storage Opcodes
EIP-11531 introduces two new opcodes, TSTORE and TLOAD, that allow contracts to use a temporary storage space that is only accessible within the same transaction. This storage space is cheaper than regular storage and does not affect the state root. The motivation for this EIP is to enable inter-frame communication between contracts without relying on calldata or regular storage, which are either insecure or costly. Some use cases for transient storage are reentrancy locks, on-chain computable CREATE2 addresses, ERC-20 approvals, fee-on-transfer contracts, and proxy call metadata.
EIP-4788: Beacon Block Root in the EVM
EIP-47882 commits the hash tree root of each parent beacon block in the corresponding execution block header. This root is stored in a smart contract that acts as an oracle for the consensus layer state. The motivation for this EIP is to provide trust-minimized access to the consensus layer for the execution layer, enabling various applications that require information about the beacon chain. Some examples of such applications are liquid staking pools, restaking constructions, smart contract bridges, and MEV mitigations.
EIP-6780: SELFDESTRUCT Only in the Same Transaction
EIP-67803 changes the functionality of the SELFDESTRUCT opcode, which allows contracts to self-destruct and recover their funds. The new functionality is that SELFDESTRUCT only deletes the contract data and transfers the funds if it is called in the same transaction as the contract creation. Otherwise, it only transfers the funds and leaves the contract data intact. The motivation for this EIP is to prepare for the transition to Verkle trees, which will make the deletion of contract data impossible. This EIP preserves the functionality of SELFDESTRUCT for contracts that use it as a reentrancy lock or a gas optimization technique.
Impacts of the Ethereum Cancun-Deneb Upgrade
The Ethereum Cancun-Deneb upgrade aims to improve the scalability, security, and efficiency of the Ethereum network, which could have various benefits for the network and its users. Some of the possible impacts of the upgrade are:
Price, Adoption, and Innovation of ETH and Other Tokens
The upgrade has the potential to boost the demand and value of ETH and other tokens on the network. This is because it may reduce transaction costs, speed up transactions, and improve the overall user experience. Additionally, the upgrade could attract more users to the network as well as see an increase in the hiring of Ethereum developers by enabling a wider range of innovative applications, such as decentralized gaming, social media, DeFi, NFTs, and more. Furthermore, it could enhance the competitiveness and interoperability of the Ethereum network by facilitating cross-chain communication and collaboration with other blockchains and platforms.
Growth and Diversity of Decentralized Applications
The upgrade has the potential to support the growth and diversity of decentralized applications on the network, as it could provide more scalability and modularity for Layer 2 solutions, such as rollups, channels, and sidechains. These solutions could leverage the data availability and security of the Layer 1 network while offering higher throughput and lower latency for transactions and smart contracts. The upgrade might also enable more complex and expressive smart contracts, as it could introduce new opcodes, data types, and storage techniques. Additionally, it could enhance e the data storage and availability of the network, as it could introduce the concept of proto-danksharding, which could allow large data packets or “blobs” to be stored and accessed on the network.
Competitiveness and Interoperability of the Network
The upgrade could enhance the competitiveness and interoperability of the network, as it could prepare the network for the future implementation of full data sharding, which is the final phase of the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade. Full data sharding could significantly boost the scalability and performance of the network, by splitting the network into smaller pieces or shards, each capable of processing transactions and smart contracts independently. This approach may also enable cross-shard communication and coordination, which could allow different shards to interact and exchange data and value with each other. Furthermore, data sharding could facilitate cross-chain communication and collaboration, which could allow the Ethereum network to connect and cooperate with other blockchains and platforms, such as Bitcoin, Polkadot, Cosmos, and more.
Challenges and Risks of the Ethereum Cancun-Deneb Upgrade
The Ethereum Cancun-Deneb upgrade is also a complex and ambitious undertaking, which could pose various challenges and risks for the network and its users, warranting a need for quality Ethereum consulting services. Here are the possible challenges and risks of the upgrade.
Technical Complexity
The upgrade involves a number of technical changes and innovations, which could introduce new bugs, errors, and vulnerabilities in the network. Achieving a successful upgrade demands a significant level of coordination and consensus among various network participants, including developers, validators, miners, users, and other stakeholders. Moreover, the success of the upgrade relies on the effective testing and deployment of both preceding and concurrent upgrades, like the Shanghai and Altair upgrades, potentially influencing the timing and overall outcome of the upgrade.
Compatibility and Integration of Existing Smart Contracts and Protocols
The upgrade may have an impact on the functionality and performance of current smart contracts and protocols on the network by introducing new opcodes, data types, and storage techniques. Gas costs and execution times for existing transactions and smart contracts could also be affected due to the introduction of new gas pricing and scheduling mechanisms. Furthermore, the security and availability of existing data and assets on the network might undergo changes with the introduction of proto-danksharding, altering the way data is stored and accessed on the network.
Unforeseen Consequences and Trade-Offs of the Upgrade
The upgrade might bring about unforeseen consequences and trade-offs for the network and its users by introducing new dynamics and incentives. For instance, it could impact the balance and distribution of power and resources among various network participants, including developers, validators, miners, users, and other stakeholders. Additionally, the upgrade could influence the trade-offs and compromises between scalability, security, and decentralization within the network, as it introduces new techniques and mechanisms for data management and transaction processing.
Suggestions and Recommendations
Considering the impacts and implications of the upgrade for the network and its users, it is advisable for the network participants to follow certain suggestions and recommendations to prepare for and cope with the upgrade.
Stay Informed and Updated
Participants in the network should keep themselves informed and up-to-date on the progress and status of the upgrade by following official channels and sources of information. These include the Ethereum blog, the Ethereum Foundation website, the Ethereum Cat Herders website, the Ethereum GitHub repository, and the Ethereum Twitter account. It is crucial for participants to remain vigilant and alert to potential scams and misinformation that may surface during and after the upgrade. Verifying the authenticity and credibility of information and sources encountered is essential to ensure accurate and reliable information.
Test and Audit the Code
The network participants are encouraged to thoroughly test and audit the code of the upgrade by actively engaging in available testnets and devnets, like the Devnet-11 and Devnet-12. Additionally, it is crucial for participants to test and audit the code of their own smart contracts and protocols using tools and frameworks designed for the upgrade, such as the Remix IDE, the Hardhat framework, the Truffle suite, and the OpenZeppelin library.
In the event of encountering or discovering issues or bugs during the testing and auditing process, participants should promptly report and resolve them. Utilizing available channels and platforms for the upgrade, such as the Ethereum GitHub repository, the Ethereum Discord server, and the Ethereum Stack Exchange site, can facilitate effective communication and issue resolution.
Back Up and Secure the Data
The participants should take measures to back up and secure their data and assets by leveraging available methods and services for the upgrade. This includes using tools like the MetaMask wallet, the Ledger hardware wallet, the Coinbase exchange, and the IPFS protocol.
Furthermore, participants are advised to encrypt and protect their data and assets using established techniques and standards applicable to the upgrade. This involves employing methods such as AES encryption, ECDSA signature, and adhering to specifications like the EIP-712 specification. Implementing these security measures helps ensure the safety and integrity of participants' data and assets on the network.
Participate and Contribute to the Network
Participants in the network are encouraged to actively participate and contribute by engaging with the community and ecosystem associated with the upgrade. This involvement can take place through platforms like the Ethereum Reddit forum, the Ethereum Telegram group, participation in Ethereum Meetup events, and involvement in Ethereum Hackathon projects.
Additionally, participants should consider supporting and contributing to the network through various mechanisms and programs available for the upgrade. This may include making use of Gitcoin grants, contributing to the Ethereum Foundation through donations, participating in the Ethereum Bug Bounty program, and exploring the Ethereum Ecosystem Support Program. Supporting and donating to the network helps foster its growth and sustainability.
Wrapping It Up
The Cancun-Deneb upgrade is a major achievement for Ethereum and the whole blockchain and crypto space. It brings Ethereum closer to its goal of becoming a scalable, decentralized, and universal settlement layer for various applications and use cases. It also shows Ethereum’s ability to innovate and adapt, using cutting-edge research and technology to improve the current network. Moreover, it reflects Ethereum’s community spirit and collaboration, involving the input and effort of many different stakeholders, such as researchers, developers, validators, users, and dApp builders.
However, the Cancun-Deneb upgrade is not the final destination for Ethereum, but rather a stepping stone toward its ultimate vision of Ethereum 2.0, which aims to make Ethereum a fully scaled, resilient, and future-proof platform. Ethereum 2.0 has several phases and milestones, such as the Beacon Chain, Shard Chains, Docking, Execution Environment, and State Execution1. These will bring new features and improvements to the network, such as switching to proof of stake, introducing data and execution sharding, merging the mainnet with the Beacon Chain, and enabling smart contracts and dApps to run on the new network.
Ethereum 2.0 is a complex and long-term project, which requires a lot of coordination and effort. It also offers many opportunities and challenges for the community, such as increasing participation and diversity, ensuring security and stability, fostering interoperability and compatibility, and maintaining innovation and development. The community will need to work together and support each other to achieve the vision and promise of Ethereum 2.0.
If you are interested in learning more about Ethereum 2.0 and how it can benefit your business, contact us today at Codezeros. We can help you leverage the power and potential of Ethereum 2.0 to create innovative and scalable solutions for your industry and customers.
Post Author

Explore Deep's insightful blog posts that help businesses stay ahead of the curve, explore new possibilities, and unlock the full potential of blockchain technology
What is Ethereum Cancun-Deneb Upgrade?
Take advantage of the latest developments in Ethereum development with Codezeors At Codezeros, our expert team constantly upgrades their skill set to align with the latest trends in Ethereum development, making us one of the safest bets in the market.



