SHARE THIS ARTICLE
Difference Between Blockchain and Cloud Computing: A Detailed Analysis
The amount of data we generate is staggering. By 2025, it’s estimated that the global digital data generated will reach an astounding 175 zettabytes – that’s 175 followed by 21 zeros! This explosion of information has brought great benefits, however, it has also raised critical questions about data security. Businesses as well as individuals are constantly searching for reliable solutions to store and manage their sensitive information.
Two technologies have come up as potential solutions – blockchain and cloud computing. Blockchain, with its distributed ledger system, promises tamper-proof data storage, while cloud computing offers scalable and on-demand access to resources. Cloud computing has been in prominence for quite a few years now, blockchain, more so in recent years. However, both fundamentally redefine how we store, manage, and interact with data.
Having said that, there is a pressing question – are blockchain and cloud computing interchangeable concepts? Or are they fundamentally different solutions? We’ll try and answer these questions in this guide. So stay tuned!
Understanding Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has become the foundation of modern IT infrastructure. In essence, it’s the on-demand delivery of IT resources – storage, processing power, databases, and even software – over the internet. Instead of managing physical servers and software licenses, businesses can rent these resources from cloud providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform. This model offers several core functionalities.
-
Storage: Cloud storage allows businesses to securely archive large amounts of data on remote servers, eliminating the need for expensive on-premise storage solutions.
-
Processing Power: Cloud computing provides access to powerful computing resources that can be scaled up or down based on processing needs. This eliminates the upfront cost of investing in high-performance hardware.
-
On-demand Access: Cloud services are accessible from anywhere with an internet connection, allowing for remote workforces and increased collaboration.
Apart from these core functionalities, cloud providers offer various service models to cater to different needs.
-
Software as a Service (SaaS): This model delivers software applications over the Internet, eliminating the need for installation and maintenance. Popular examples include Salesforce for CRM or Google Workspace for productivity tools.
-
Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS provides a platform for developing, deploying, and managing applications. Developers can utilize pre-built tools and infrastructure without worrying about the underlying hardware.
-
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): This model offers the most basic building blocks: virtual servers, storage, and networking resources. Businesses have complete control over the environment and can customize it for their specific needs.
For businesses, cloud computing offers a compelling value proposition. Scalability is a key benefit – resources can be easily scaled up or down as business needs fluctuate. This eliminates the risk of over-positioning hardware and reduces overall IT costs. Moreover, cloud services are typically pay-as-you-go, further improving cost efficiency. Accessibility is another major advantage. Cloud-based applications and data can be accessed from any device with an internet connection, facilitating remote work and improved collaboration.
However, security considerations remain a critical aspect of cloud adoption. Data breaches can occur if proper security measures are not implemented. Furthermore, "vendor lock-in" can be a concern, where businesses become overly reliant on a specific cloud provider's platform, making it difficult and costly to switch in the future.
Understanding Blockchain Technology
Cloud computing offers a flexible and scalable approach to data storage and access, but what if trust in a centralized authority is a concern? A Blockchain development company can solve this issue. At its core, blockchain is a distributed ledger – a digital record of transactions that is duplicated and distributed across a network of computers.
How It Works
Information is grouped into "blocks," which are then cryptographically linked together in a chronological chain. Each block contains data about the transaction, a timestamp, and a unique fingerprint (hash) of the previous block. This creates a tamper-proof record, as any attempt to alter a block would invalidate the entire chain.
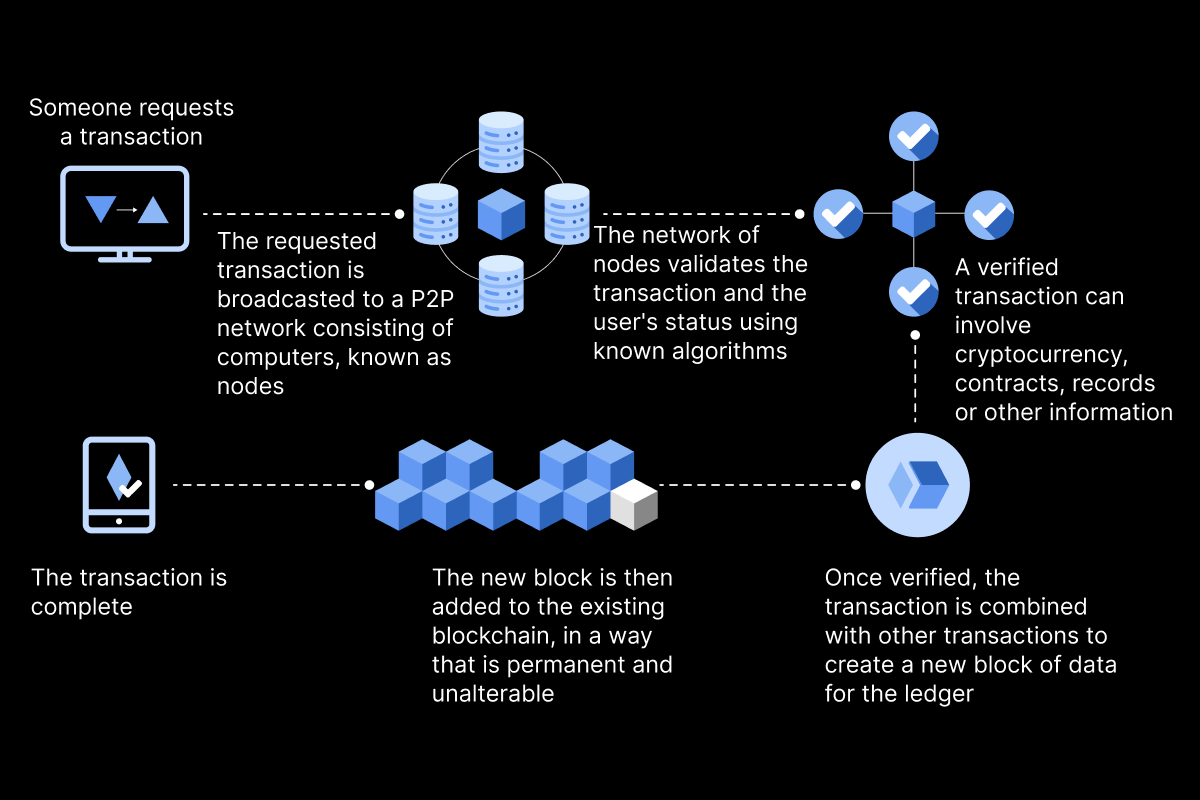
To ensure consistency and security across the network, a consensus mechanism is used. This mechanism determines how participants in the network agree on the validity of new transactions. Here are some of the more prominent consensus mechanisms.
-
Proof of Work (PoW): This method requires miners to solve complex mathematical puzzles to add new blocks to the chain. While secure, PoW is computationally intensive and energy-consuming.
-
Proof of Stake (PoS): Here, the likelihood of validating a block is based on the amount of cryptocurrency a user holds (their stake). This reduces energy consumption compared to PoW.
Advantages of Blockchain Technology
-
Transparency: All participants on the network can view the entire transaction history, promoting trust and accountability.
-
Immutability: Once recorded, data on a blockchain cannot be altered or deleted, reinforcing data integrity.
-
Security: Cryptography and distributed ledger technology make it highly resistant to hacking and manipulation.
However, there are a few limitations of blockchain technology as well. Scalability is a major concern – processing transactions on a blockchain can be slower than traditional methods. Additionally, some blockchain implementations can be energy-intensive due to consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work.
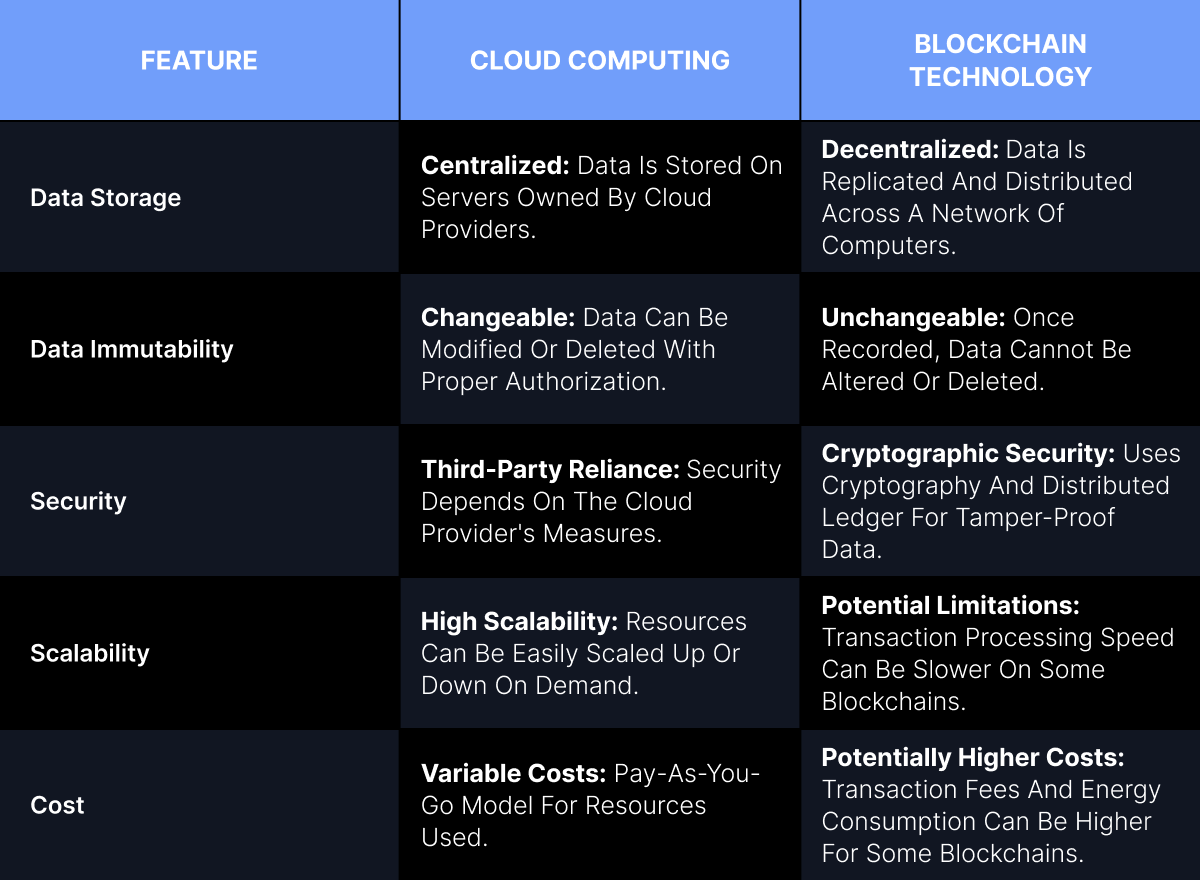
Blockchain vs Cloud Computing
While both cloud computing and blockchain offer solutions for data storage and management, they operate on fundamentally different principles. Here's a breakdown of their key differences.
Real-World Applications
The widespread adoption of digital technologies has altered data management and sharing practices. Cloud computing and blockchain technology are driving this transformation, each providing distinct advantages that are having a transformative impact on businesses across various sectors.
Cloud Computing's Scalable Solutions
Cloud computing's ability to provide on-demand, scalable resources makes it a preferred choice for several enterprise applications.
-
Data Storage: Businesses of all sizes can tap into cloud storage solutions like Dropbox or Google Drive to securely archive and manage massive datasets. This eliminates the need for capital expenditures on physical storage infrastructure and simplifies data accessibility for authorized users.
-
Application Deployment: Cloud platforms like Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Microsoft Azure offer robust infrastructure and tools that allow companies to deploy and manage applications with greater agility and efficiency. This reduces development time and costs associated with maintaining on-premise servers.
-
Enhanced Remote Collaboration: Cloud-based productivity tools like Google Workspace or Microsoft 365 empower geographically dispersed teams to collaborate effectively in real time. This promotes improved communication and document sharing, optimizing workflows and boosting overall productivity.
Blockchain's Disruptive Potential
While cloud computing excels in managing and scaling IT resources, blockchain service providers disrupt industries by establishing trust and transparency in ecosystems where it has traditionally been lacking.
-
Supply Chain Management: Blockchain can track the movement of goods from origin to destination, ensuring product authenticity and provenance. This minimizes the risk of counterfeit products entering the supply chain, improving overall efficiency and consumer confidence.
-
Secure Voting Systems: Blockchain technology can be utilized to create tamper-proof voting systems, where votes are immutably recorded on a distributed ledger. This considerably reduces the risk of manipulation and fraud, strengthening the integrity of the democratic process.
-
Digital Asset Management: Blockchain forms the foundation for cryptocurrencies and facilitates secure ownership and transfer of digital assets. This opens doors for innovative applications in areas like digital art, music ownership, and even fractional ownership of real estate.
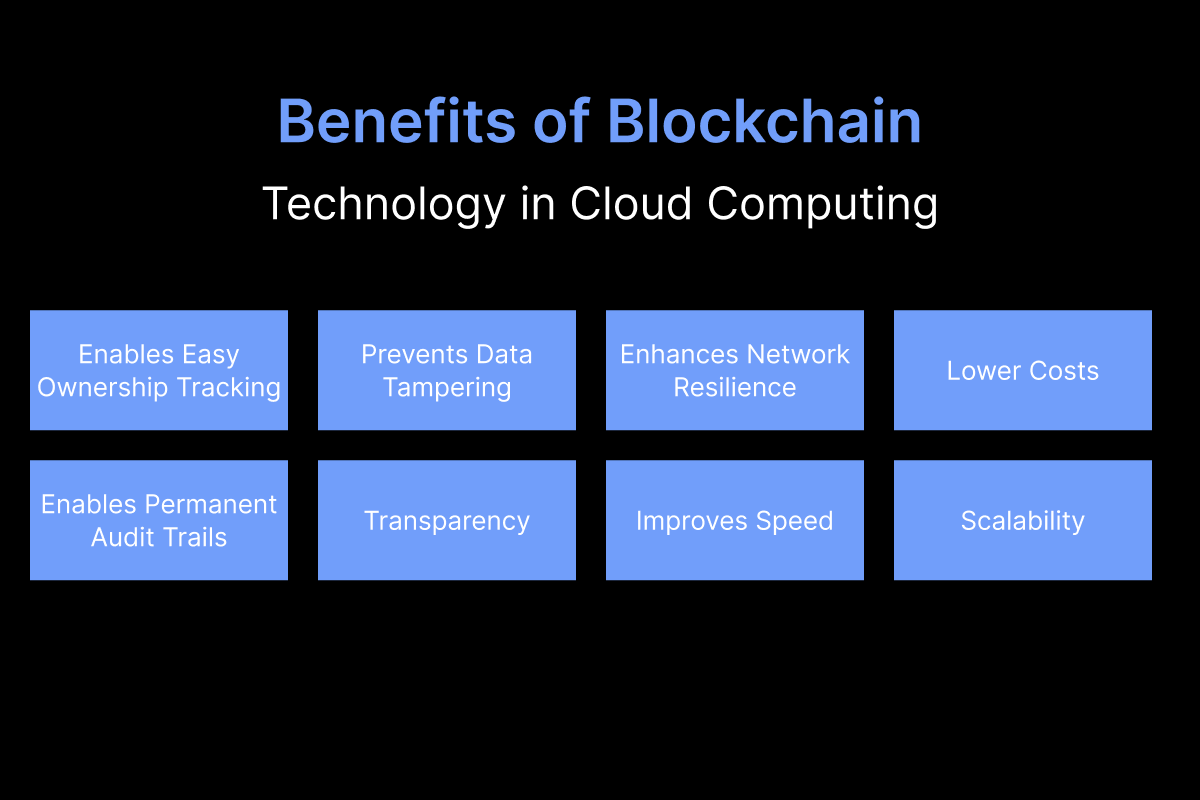
The Future Outlook – Convergence or Competition?
Cloud computing and blockchain occupy distinct niches within the technological space, but there's a growing potential for them to work together synergistically.
Hybrid Cloud Models
The concept of hybrid cloud models or blockchain cloud technology is gaining traction. This approach taps into the strengths of both technologies – the scalability and flexibility of cloud computing alongside the security and transparency of blockchain. For instance, a business might store sensitive data on a private blockchain while utilizing cloud resources for everyday operations. This creates a secure and efficient data management ecosystem.
Cloud Providers Adopt Blockchain
Several major cloud providers are already exploring ways to integrate blockchain technology into their offerings. Microsoft Azure offers Blockchain as a Service (BaaS) solutions, allowing businesses to build and deploy blockchain applications on the Azure cloud platform. This trend is likely to continue, with cloud providers offering effective tools and infrastructure for developers building blockchain-based solutions.
Co-existence for a Secure and Efficient Future
Ultimately, cloud computing and blockchain are rather complementary solutions. Cloud computing provides the foundation for scalable and accessible data storage and processing power. Blockchain, on the other hand, offers a secure and transparent way to record and manage transactions. By tapping into their unique strengths these technologies can work together to create a more secure and efficient future for data management.
However, it is crucial for businesses to understand the distinct capabilities of cloud computing and blockchain technology. By choosing the right tool for the job, or even employing a hybrid approach, businesses can facilitate secure, transparent, and scalable data management for years to come.
At Codezeros, we can help you tap into both cloud and blockchain technologies to deliver innovative solutions. Whether you're looking for secure and scalable cloud storage solutions, or blockchain-powered applications for improved transparency and trust, our team of experts can help you identify the right technology to meet your specific needs.
Contact us today for a free consultation to discuss your specific needs
Post Author

Explore Deep's insightful blog posts that help businesses stay ahead of the curve, explore new possibilities, and unlock the full potential of blockchain technology
Tap into cloud-based blockchain solutions from Codezeros.
Cloud-based blockchain is the safest bet when scalability and flexibility are essential considerations. Codezeros offers blockchain solutions designed to accelerate growth, improve security, and optimize operations.



